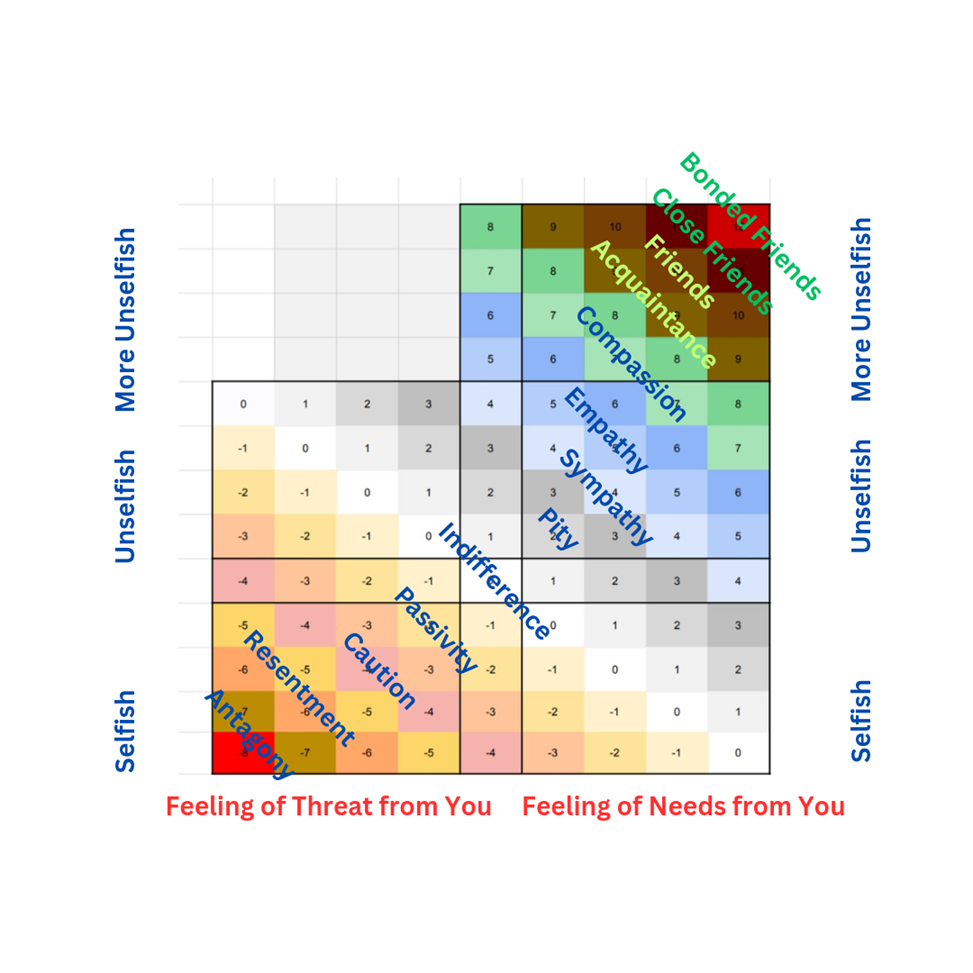
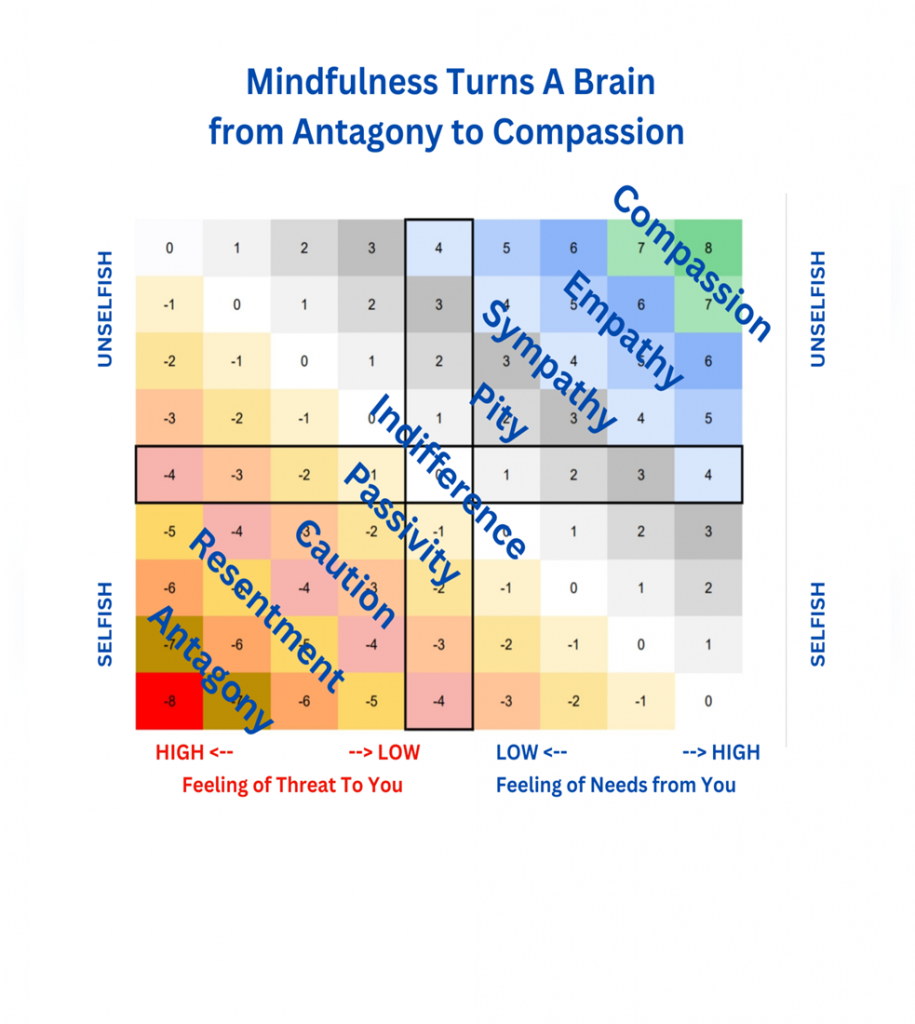
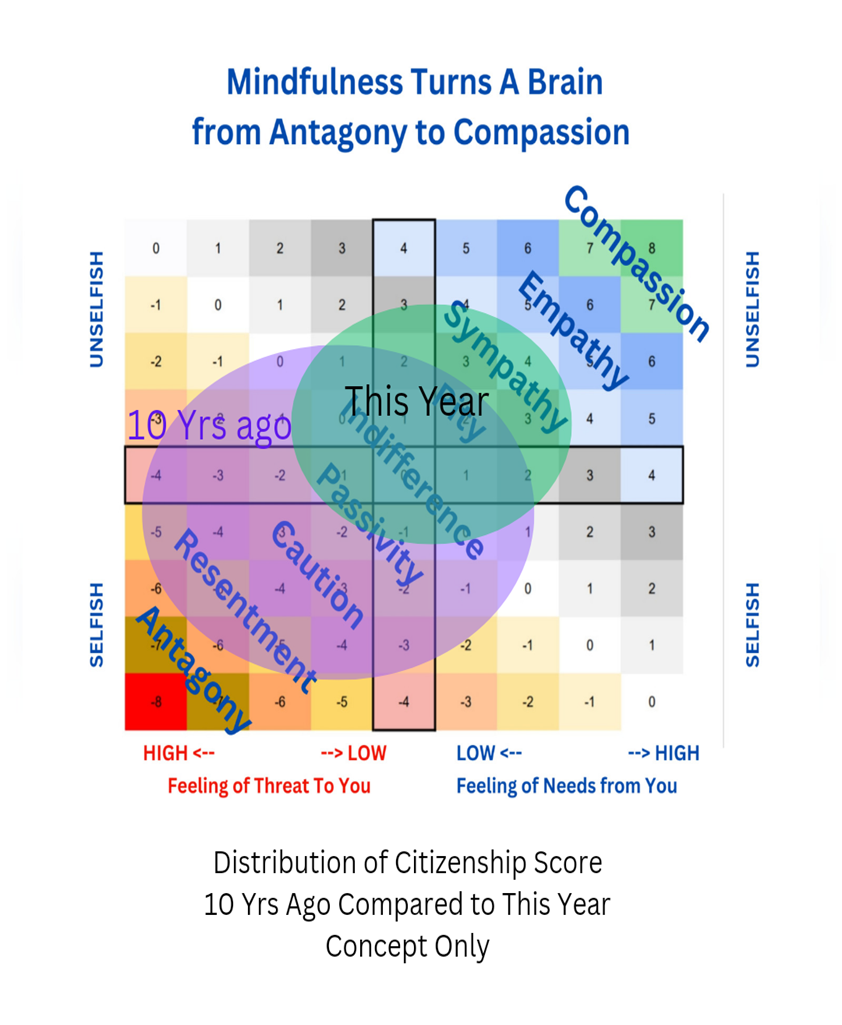
What could possibly go wrong with this sunny picture? First up is Butch Hancock, who said: ““Life in Lubbock, Texas taught me two things: One is that God loves you and you’re going to burn in hell. The other is that sex is the most awful, filthy thing on earth, and you should save it for someone you love.” https://www.goodreads.com/quotes/508980-life-in-lubbock-texas-taught-me-two-things-one-is, last visited May 26, 2025.
Millions or even billions fear God and even point to their fear as a source of pride: “I’m a God-fearing Christian.” I ask: “Is it consistent to fear the perfect man?” Why wouldn’t you trust the perfect man, who is your friend, to be at least fair and in all likelihood merciful and forgiving. Allowing or even causing the teeming billions of the Lord’s creations and friends to burn in hell forever surely seems strictly out of bounds.
This is a version of the so-called problem of evil. Theodicy is the field devoted to explaining away the problem of evil. One way is to say we are just in a test and those who pass the test get to go to heaven instead of roasting forever in hell. Why an omniscient being like God needs a test to get results is left unexplained? Some suggest free will is involved, specifically, that God loves us so much that he gave us a fair opportunity to earn a ticket to hell, and without warning us in the clearest of terms possible for an omnipotent being that such a fate awaits many or even almost all of us.
But let’s bring things back to earth. Next up in our list of witnesses is Jennifer Willoughby. She describes her experience, which I find eminently believable. Believe the women, some urge. So, let us at least try to do so. Here’s her story in a moving nutshell, the nub of her gist.
“[H]e could be kind and sensitive. And so I stayed. He cried and apologized. And so I stayed. He offered to get help and even went to a few counseling sessions and therapy groups. And so I stayed. He belittled my intelligence and destroyed my confidence. And so I stayed. I felt ashamed and trapped. And so I stayed. Friends and clergy didn’t believe me. And so I stayed. I was pregnant. And so I stayed. I lost the pregnancy and became depressed. And so I stayed.” ~ Jennifer Willoughby, speaking of her allegedly abusive husband Rob Porter (Republican, Mormon, Harvard University, B.A., J.D., New College, Oxford: Oxford University, M.Phil.), appearance on The Last Word with Lawrence O’Donnell, MSNBC, February 8, 2018.
Friendships often end badly or become exploitative. To exploit someone is to take unfair advantage of their predicament, to give a rough and ready, short and snappy, down and dirty first approximation of a definition of exploitation. Consult your experience and ask yourself, seriously ask yourself as Philosophy demands, if Willoughby’s experience resonates with you as believable, and if her experience has parallels or analogies with some friendships you have experienced. Talk amongst yourselves while I move on, since I’m scarcely done.
One might object to my damn, fool questions and examples by insisting that friendship involves loyalty and what could possibly be wrong with that, especially in the world we live in now chock full of porn websites and dating websites urging us to explore alternatives rather than loyally hang around with the person who happens to be your romantic friend at the moment. As Stephen Stills sang, “If you can’t be with the one you love, love the one your with.” And websites make it push-button easy to get together. It’s just lunch? But is the service arranging lunch with someone of your designated range of ages, interests, locations, etc. really just lunch or is it a portal to another friendship or at least to an experiment in friendship or trying to make friends.
Dale Carnegie earned some wealth showing us in a book how to win friends and influence people. Well, surely any prize you win in the great capitalist countries of the world at least must be worthwhile. So, friendship must be worthwhile, especially since it involves a good measure of loyalty.
But the above is a procedural argument. We’re following capitalist procedures to win friends and spawn loyalty. We are allowed, however, to look at results rather than just have tunnel vision about procedure. We need simply ask a few pointed questions about loyalty to see that loyalty is not all it is cracked up to be. Millions were loyal to Hitler. Hundreds or even thousands were and are loyal to the worst gangsters. Hundreds of millions are loyal to questionable, to say the least, politicians such as LBJ, Nixon, or Trump. Is such loyalty and friendship really so good that it is beyond serious question? Very well, what about the loyalty and friendships in religious cults? Consider Jim Jones’ Jonestown, David Koresh’s Branch Davidians in Waco, Texas (have you noticed that we keep coming back to Texas?), Marshall Applewhite’s Heaven’s Gate cult in the suburbs of San Diego. OK, we keep coming back to California, too. The problem of overestimating the value of friendship, as if it is scarcely a double-edged sword, is bi-coastal, and bipartisan, since we find it in red and blue states alike.
And then there step forward the enablers. Many friends, out of friendship or even love, enable their closest friends or relatives to stay addicted to dangerous substances, all too often leading to death. Suicide among the young is at an all-time high in America. Guns are the leading cause of death among children. Relying on mere friendship to get us out of this mess is, as a piece of friendly advice from me to you, naïvely and overly optimistic in a way that brings us right back to the critical thinking of Voltaire’s Candide. Discuss all this with your friends.
________________________________________________________________
The Dark Side of Friendship by ChatGPT
ChatGPT: The dark side of friendship often emerges in ways that contrast sharply with the idealized view of friendship as inherently supportive, positive, and enriching. When certain dynamics shift, friendships can lead to stress, hurt, and even harm. Here are some common aspects of this darker side:
1. Envy and Competition
- Sometimes, friendships can foster competition, with one person feeling the need to outshine or “win” over the other. Envy can creep in when friends are at different stages of success or life milestones, leading to resentment and feelings of inadequacy. This competition often goes unspoken, making it difficult to address and potentially harming both parties.
2. Emotional Dependency and Toxicity
- Some friendships develop a dependency where one person becomes overly reliant on the other for emotional support or validation. This can drain the energy of the friend who becomes a constant shoulder to lean on, eventually leading to resentment. When one friend’s needs consistently overshadow the other’s, the relationship may become toxic, resembling a one-sided dependency instead of a balanced, healthy connection.
3. Betrayal and Breach of Trust
- One of the most painful experiences in friendship is betrayal, which can take the form of gossip, secrets shared without permission, or other actions that compromise trust. Once breached, trust is challenging to rebuild and can lead to lingering insecurities and doubts, not only in that friendship but also in future relationships.
4. Manipulation and Control
- In some friendships, one person may seek to control or manipulate the other, whether consciously or unconsciously. This might manifest through guilt-tripping, constant criticism, or dictating what the other person should do. Such manipulation can erode a friend’s self-esteem and sense of autonomy, leaving them feeling trapped rather than supported.
5. Outgrowing Each Other
- As people grow and change, sometimes friends no longer fit each other’s lives in the same way. This evolution can create tension, especially if one friend resists or resents the change. Trying to force the friendship to stay the same can prevent both friends from growing and even create animosity where there was once a camaraderie.
6. Enabling Unhealthy Behavior
- Some friendships are built on shared habits or interests that can be harmful, such as substance abuse, negative self-talk, or reinforcing poor life choices. In these cases, friends may encourage or validate each other’s unhealthy behaviors, preventing either from making positive changes.
7. Loyalty at a Cost
- Loyalty is often valued in friendship, but in some cases, it can be detrimental. Unquestioning loyalty can prevent someone from seeing red flags, ignoring hurtful behavior, or staying in situations that are harmful out of a sense of obligation.
8. Friendship for Convenience
- Sometimes, friendships persist out of convenience rather than genuine affection. This can be the case in friendships formed at work, in school, or out of routine. When the practical reason for the friendship ends, the superficial connection can become a source of awkwardness or discomfort.
9. Influence on Self-Identity
- Friendships shape self-perception, for better or worse. When a friend projects their insecurities or limitations onto the other, it can influence their friend’s self-identity in damaging ways. Over time, these interactions may contribute to limiting beliefs or self-doubt.
Exploring these darker aspects can make us more aware of potential red flags, as well as help us develop healthier boundaries and self-awareness in our relationships. Understanding the full scope of friendship—the light and the dark—helps us foster connections that are both genuine and sustainable.
__________________________________________________________________________
Set Boundaries or Space, but Not to Cut off Completely & Permanently. Treasure what has been or had been positive before. Good Memories are Precious,
ChatGPT: Absolutely. Setting boundaries or taking space in a friendship doesn’t have to mean cutting ties or forgetting the good times you’ve shared. Friendships, like all relationships, can go through phases, and sometimes giving each other room to grow individually is necessary to keep the bond healthy. When we focus on boundaries as a way to protect ourselves and the relationship, rather than as a way to “end” things, we allow room for both parties to feel secure without erasing the meaningful parts of the connection.
Here’s how to navigate this balance:
1. Acknowledge and Honor the Good Times
- Reflecting on what made the friendship meaningful—like shared memories, laughter, and support—helps remind both of you why the relationship matters. It can soften difficult conversations and help approach the situation with gratitude rather than frustration.
2. Communicate Openly about Boundaries
- It can be powerful to share, kindly and honestly, what you’re feeling. Saying something like, “I need some time for myself right now, but I really value our friendship,” reinforces that the space is for individual well-being, not a desire to break the bond.
3. Set Boundaries with Compassion
- Boundaries don’t have to be rigid or harsh. For example, setting limits around certain topics of conversation, types of support, or frequency of contact can keep the friendship from feeling overwhelming without closing the door completely. Compassionate boundaries allow you to be clear about your needs in a way that respects both of you.
4. Give Space without Guilt
- Allowing for space without resentment or guilt can be incredibly free. It’s natural to miss each other, but knowing the purpose of space can help it feel like a temporary recharge rather than a permanent loss.
5. Appreciate What’s Gone Well, even if Dynamics Change
- Even if a friendship doesn’t look the same as it once did, that doesn’t mean good memories are any less valuable. Embracing that friendships evolve allows you to treasure the positive moments without feeling that they’re lost or invalidated by change.
6. Check In Occasionally
- Even if you’re taking a break, a small gesture—a message, a memory shared, or a quick hello—can maintain the connection at a healthy distance. It lets both of you know that friendship still matters, even as you honor new boundaries.
Creating this balance is ultimately a way to protect what’s good in the friendship without sacrificing personal well-being. Boundaries and space, handled with respect and appreciation, are not just ways to maintain the connection; they’re ways to ensure that the best parts of the friendship continue to be cherished and preserved
_________________________________________________________________.______________________